Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger: A Comprehensive Guide
by AMC
Posted on December 10, 2024 at 05:01 PM
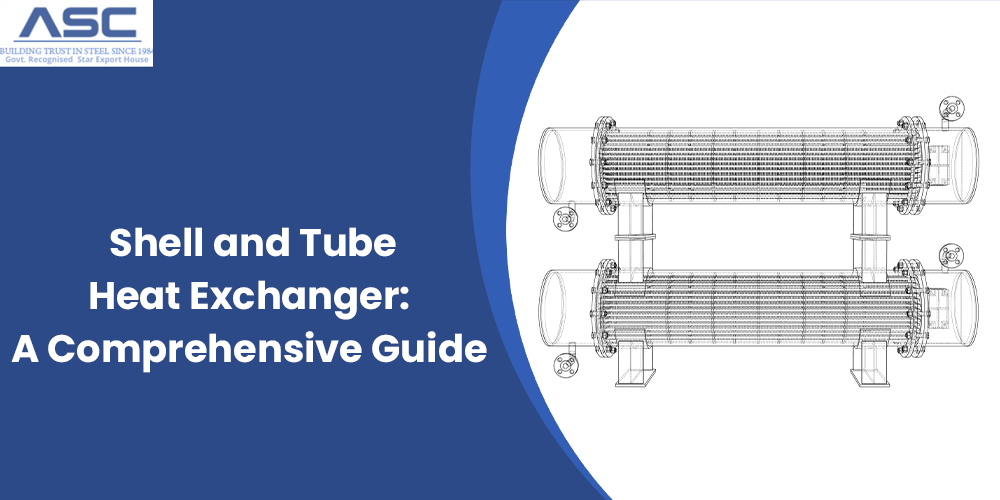
Shell and tube heat exchangers are essential components in thermal processing systems, designed to transfer heat between fluids efficiently. heat exchangers are widely used in oil refining, chemical processing, and power generation industries.
This guide will explore how shell and tube heat exchangers work, their design features, applications, key advantages, and important maintenance considerations to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
What is a Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger?
A shell and tube heat exchanger is a device used to transfer heat between two fluids. It has a large outer shell with several tubes inside. One fluid flows through the tubes, while the other flows around them inside the shell. This design helps exchange heat efficiently. These heat exchanger tubes are widely used because they are effective and can be customized for different needs.
Shell and tube heat exchangers are popular because of their simple design and efficient heat transfer. They work by moving fluid or steam through the shell, which heats the tubes inside. For the best performance, the fluid is usually passed through the tubes four times, which ensures effective heat transfer.
Understanding Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger Design
Shell & tube heat exchanger designs are among the most versatile and widely used devices for heat transfer in industrial processes. Their design, ability to handle high pressures, and adaptability across multiple applications make them a preferred choice in various industries. Let’s delve into their operating principles, key applications, advantages, and maintenance requirements.
Operating Principles of Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers
Shell and tube heat exchangers operate by transferring heat between two fluids. One fluid flows through the tubes (tube side), while the other flows around the tubes inside the shell (shell side). Depending on the flow pattern, these heat exchangers can work in two configurations:
- Counterflow: Fluids move in opposite directions, ensuring maximum temperature difference and higher heat transfer efficiency.
- Parallel Flow: Fluids flow in the same direction, offering less efficient heat transfer compared to counterflow.
Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger Applications Across Industries
Shell and tube heat exchangers are indispensable in industries due to their ability to manage diverse temperature and pressure conditions. Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger Applications include:
- Petrochemical Industry: Vital for refining processes like condensation, distillation, and heating of fluids.
- HVAC Systems: Used to regulate air temperature and humidity in heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems.
- Power Generation: Essential in boilers, condensers, and cooling systems for heat transfer between steam and water.
- Food Processing: Widely used for pasteurization, sterilization, and cooling in the dairy, beverage, and pharmaceutical industries
Why Choose Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers from Amardeep Steel?
Amardeep Steel is a leading supplier of high-quality shell and tube heat exchangers designed to meet the diverse needs of industries worldwide. With expertise in manufacturing and sourcing premium materials, Amardeep Steel ensures durability, efficiency, and performance in every product. Whether you need custom-built designs or standard configurations, their solutions cater to all industrial requirements.
Maintenance Tips for Optimal Performance
To ensure the longevity and efficiency of shell and tube heat exchangers:
- Regular Cleaning: Prevents fouling and maintains heat transfer efficiency.
- Inspect Tubes Regularly: Check for leaks, corrosion, or damage to avoid system failures.
- Monitor Performance: Keep track of temperature differentials and flow rates to identify and address issues early.
Conclusion
Shell and tube heat exchangers are vital for efficient heat transfer in numerous industries. With their durability, adaptability, and high performance, they are a reliable solution for complex thermal processes. For premium-quality heat exchangers and exceptional service, shell and tube heat exchanger manufacturers trust Amardeep Steel, a leader in delivering solutions to meet your industrial needs.
FAQs
1. What is the working principle of a heat exchanger?
Principles of heat exchangers
Heat exchangers work because heat naturally flows from higher temperatures to lower temperatures. Therefore if a hot fluid and a cold fluid are separated by a heat-conducting surface heat can be transferred from the hot fluid to the cold fluid.
2. What is the difference between shell side and tube side?
Shell and tube exchangers have a number of tubes mounted inside of a shell. One fluid flows through the tubes (tube side) while the other flows over the outside of the tubes (shell side). Baffles are used on the shell side to increase turbulence, prevent stagnation, and improve the heat transfer rate.
3. What are the advantages of shell and tube?
Advantages: High Efficiency: Shell and tube heat exchangers offer efficient heat transfer due to their large surface area and turbulent flow. Versatility: They can handle high pressures and temperature differentials, making them suitable for various applications.

Boiler Tube Material Specification
Boiler Tubes are important for many industries, especially in steam boilers, power plants, and factories. Boiler Tubes are made from carbon steel or alloy

